Endocrine Disorders
Information related Endocrine Disorders.
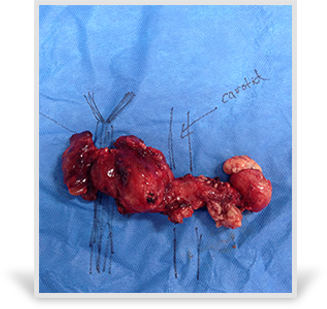

Thyroid Goiter
A goiter simply means growth in the thyroid. It does not convey any determination of the size of the thyroid or of function. A person can have abnormal blood work but have a completely normal thyroid on ultrasound. Conversely, a person can have growths within the thyroid and completely normal blood work. This highlights the importance of ultrasound in thyroid screening. Growths may be benign or malignant. Even in benign cases, the growths can causes issues related to breathing, swallowing, and voice because of proximity to important surrounding structures.
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is among the fastest growing in incidence cancers in the United States currently. People may not be getting more cancer; however, with the widespread use of ultrasound, CT, MRI, and PET scans, thyroid growths are commonly detected. There are four different types of thyroid cancer: papillary, follicular (or Hurthle cell), meduallary, and anaplastic. Although they seem to get equal play on the internet, most patients either have papillary or follicular cancers. Patients can be treated with minimally invasive surgery to remove the cancers and surrounding lymph nodes. Patients with papillary or follicular cancers may also need therapy with radioactive iodine to prevent recurrence. Long term thyroid hormone supplementation is necessary.
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s is a common cause of hypothyroidism. It is similar to Graves but the end result is under production of thyroid hormone through autoimmune processes. Symptoms include weight change, fatigue, hair loss, brittle nails, constipation, difficulty paying attention, infertility, and body aches. It is sometimes diagnosed with blood testing. Patient have a high TSH, low T3 and T4 levels, and elevated thyroid peroxidase antibody levels. Surgery is reserved for patients with symptoms of compression, concern for cancer, or who cannot be appropriately medically managed.
Hyperparathryoidism
Hyperparathryoidism is a condition in which one or more of the parathyroid glands overproduce parathyroid hormone. Parathyroid hormone is important in the regulation of calcium for the body. Bengin tumors can form on the parathyroid glands causing the body to continually take calcium out of the bones and release the calcium into the blood stream. Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism include kidney stones, cardiovascular disease, osteopenia, osteoporosis, bone fractures, bone pain, fatigue, depression or memory issues.
